Did you know that 70% of human activity and energy originates from the feet? Not only that, but 50% of the nerves and blood vessels in the human body are located in the feet, with 50% of the blood flowing through them.
Essentially, your feet are the primary centers of movement for your body. The largest and strongest joints and bones in the human body are found in the feet. Therefore, it’s crucial for your legs to be active and strong. This is why most doctors recommend daily walking. If you neglect this, you could fall victim to a disease like ‘Sarcopenia’, which involves the loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength. This can be even more detrimental than osteoporosis.
The most rapid damage from sarcopenia begins in the muscle of the legs, because when a person sits or lies down, the legs are not moving and the muscle strength of the leg muscle is affected.
let’s talk about sarcopenia…
What is Sarcopenia?,
Sarcopenia is a medical condition characterized by the gradual loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength, typically affecting individuals aged thirty and older. In essence, it is ‘Muscle Loss With Aging’, but it can be even more dangerous than osteoporosis. With osteoporosis, the primary concern is avoiding falls, whereas sarcopenia not only affects quality of life but also can lead to high blood sugar due to insufficient muscle mass. In fact, diabetes mellitus and sarcopenia are increasing health concerns in the elderly. They share pathophysiological mechanisms and each individually increases the risk of cardiovascular complications and death.
Sarcopenia intensifies around age 75 and contributes to frailty, increasing susceptibility to falls and fractures. Signs and symptoms include weakness, fatigue, loss of energy, balance problems, and difficulty walking and standing (meaning you may fall even while standing).
Sarcopenia can affect your gait, balance, and overall ability to perform daily tasks. It is strongly linked to physical disability, poor quality of life, and even death. Symptoms may include weakness and loss of stamina, which may interfere with physical activity. Regular exercise, especially resistance training, and a protein-rich diet can help reduce the consequences of sarcopenia and preserve muscular health as you age.
Although sarcopenia is common in older people, it can also affect younger individuals. Aging is the cause of primary sarcopenia. Secondary sarcopenia can have multiple causes, including lack of activity, age-related decline in testosterone, genetic factors, and insufficient energy or protein intake due to anorexia or malabsorption. Sarcopenia lasting for at least six months is considered chronic.
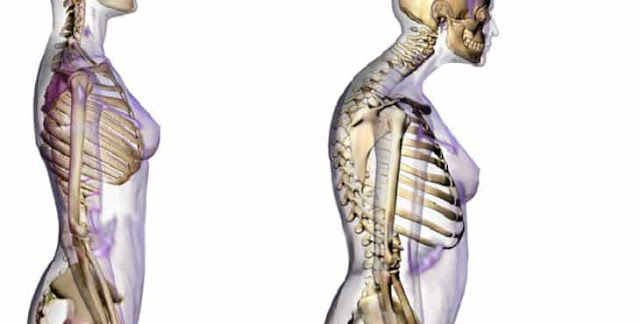 |
Sarcopenia
is characterized by loss of muscle mass
Lethal Effects of Sarcopenia,
Sarcopenia is not only associated with the progressive
loss of muscle strength, mass, and function, but it is often exacerbated by
chronic comorbidities including cardiovascular and respiratory diseases,
chronic kidney disease, and cancer, with a higher risk of mortality, falls
and fractures, metabolic problems, and cognitive impairment. It can
significantly reduce the quality of life, especially in older adults.
What are the Causes of Sarcopenia and how is it Diagnosed?,
The main causes of sarcopenia include decreased physical activity, hormonal changes, poor diet, a sedentary lifestyle, age-related muscle changes, and neurodegenerative changes (a decrease in the nerve cells that send signals from your brain to tell your muscles to move). The intrinsic molecular mechanisms of aging, chronic illness, malnutrition, and immobility are also associated with the development of sarcopenia.
 |
Sarcopenia causes loss of muscle mass,
determining important alterations that determine the loss of muscle strength.
Is sarcopenia treatable?,
Yes, sarcopenia is treatable. The main treatment path for sarcopenia is exercise, specifically resistance training. This form of exercise is designed to improve muscle strength and stamina and uses resistance bands or weights². Resistance training can also help balance your hormone levels and has been shown to improve the ability to turn protein into energy in older people.
In addition to exercise, a healthy diet and adequate protein intake are also important in maintaining muscle mass.
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can help to raise lean body mass, decrease abdominal fat, and prevent bone deterioration in women whose hormone levels decrease with menopause. However, the use of HRT is debated because of an increased risk of some cancers and other severe health conditions.
There are other treatments under investigation, including growth hormone supplements, testosterone supplements, hydroxy methylbutyrate, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, vitamin D medications, creatine to increase and maintain muscle mass, and medications for the treatment of metabolic syndromes. If these prove useful, they'll be used in conjunction with resistance training, not in place of it.
It is recommended that individuals in the high-risk category incorporate lifestyle changes, regular exercise, and a balanced diet to reduce the likelihood of muscle loss. In fact, elderly patients with diabetes are advised to undergo screenings for sarcopenia to promptly receive care to address the combined threat of these conditions. Currently, there are no approved medications for sarcopenia, so treatment strategies typically involve periodic medical assessments and lifestyle strategies.




.png)
.jpg)
.png)



0 Comments